Contents
Introduction to Partition Tables in SQL Server
In the fast-evolving landscape of database management, the use of partition tables in SQL Server has emerged as a powerful strategy. These tables provide a way to organize and manage large datasets efficiently, offering benefits such as improved query performance and simplified maintenance tasks.
Advantages of Using Partition Tables
Partition tables bring several advantages to the table, pun intended. The foremost benefit is the enhancement of query performance. By dividing a large table into smaller, more manageable partitions, SQL Server can execute queries more swiftly. This is particularly beneficial for databases dealing with extensive datasets where traditional tables might struggle to maintain optimal performance.
Efficient data management is another significant advantage. Partitioning allows for the isolation of subsets of data, making it easier to perform maintenance tasks on specific sections without affecting the entire dataset. This granularity simplifies operations like backups, indexing, and archiving.
How to Create a Partition Tables in SQL Server
Creating a partition table in SQL Server involves a straightforward process. To embark on this journey, follow these step-by-step instructions:
-- Creating a partition table
CREATE TABLE SalesData
(
ID INT,
ProductName VARCHAR(255),
SaleDate DATE,
SaleAmount DECIMAL(10,2)
)
ON PartitionScheme(SalesPartitionScheme(SaleDate))In this example, a partition table named SalesData is created, and it’s partitioned based on the SaleDate column using the SalesPartitionScheme.
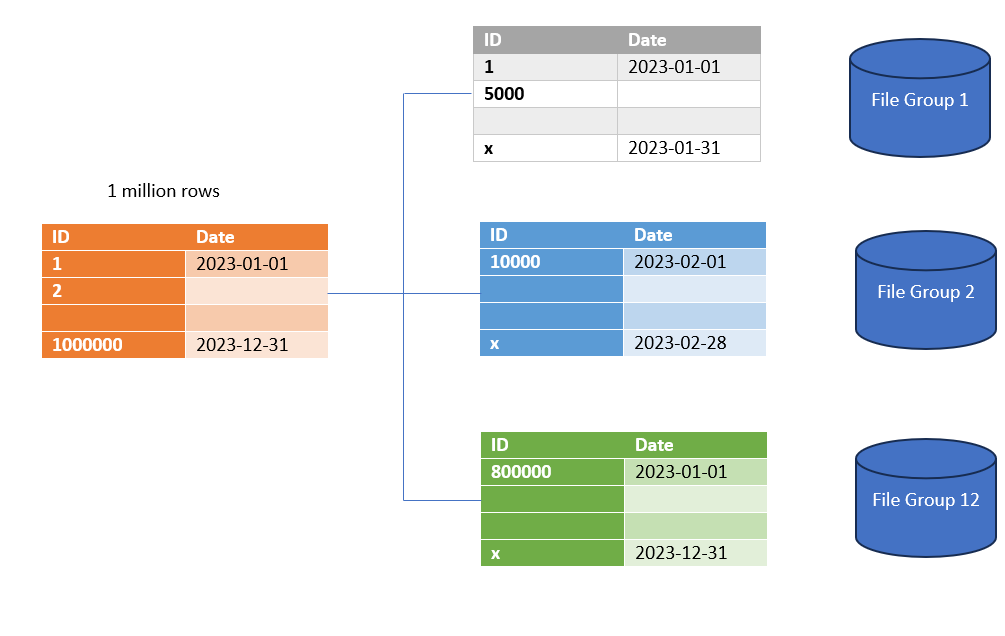
Choosing the Right Partitioning Key
Selecting the appropriate column as the partitioning key is crucial for the effectiveness of partition tables. The chosen column should align with the query patterns and distribution of data. Factors such as data distribution, query performance, and maintenance operations should be considered in this decision-making process.
Common Partitioning Strategies
There are several partitioning strategies to choose from, each suitable for different scenarios:
- Range Partitioning: Divides data based on a specified range of values.
- List Partitioning: Partitions data using a predefined list of values.
- Hash Partitioning: Distributes data evenly using a hash function.
- Composite Partitioning: Combines multiple partitioning methods for complex scenarios.
Understanding the nature of your data and query patterns will guide the selection of the most appropriate partitioning strategy.
Managing and Maintaining Partition Tables
As your data evolves, so should your partition tables. Here are some essential operations for managing and maintaining partitioned tables:
Adding and Removing Partitions
Adding or removing partitions allows for dynamic adjustments to the table structure. This is particularly useful when dealing with changing data patterns or adding historical data.
Adding a Partition:
Let’s say you have a table named “YourTable” with a partitioned column named “YourPartitionColumn“. Now, you want to add a new partition for values greater than 100:
ALTER TABLE YourTable
ADD PARTITION RANGE (YourPartitionColumn > 100);Removing a Partition:
To remove a partition, you need to use the MERGE statement to merge the partition you want to remove with its neighboring partition. Here’s an example:
ALTER TABLE YourTable
MERGE RANGE (YourPartitionColumn <= 100);Splitting and Merging Partitions
Splitting and merging partitions enable finer control over data organization. These operations are handy for adapting to changing business requirements or optimizing data storage.
Handling Data Archival in Partitioned Tables
Archiving data is simplified in partitioned tables. Older partitions, representing historical data, can be easily moved to archival storage, keeping the active dataset lean and responsive.
Querying Data from Partition Tables
Optimizing queries for partitioned tables is crucial to harness the full potential of this database management strategy. Consider the following tips for efficient data retrieval:
- Leverage the partition key in WHERE clauses to prune unnecessary partitions.
- Use partition elimination to skip irrelevant partitions during query execution.
- Keep statistics updated to aid the query optimizer in making informed decisions.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Partition Tables
Effectively monitoring and troubleshooting partitioned tables require the right tools. SQL Server provides various mechanisms for tracking the health and performance of partitioned tables. Regularly monitor partition sizes, query execution times, and disk usage to identify and address any issues promptly.
Best Practices for Partition Table Implementation
Implementing partition tables is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Adhering to best practices ensures a smooth experience and optimal performance:
- Choose the Right Partitioning Column:
- Select a column that is frequently used in queries and has a high cardinality (a large number of distinct values).Date or time columns are often good choices, as they are commonly used in range queries.
CREATE TABLE YourTable ( ID INT, YourPartitionColumn DATETIME, -- Other columns ) - Define Appropriate Partitioning Ranges:
- Partitioning ranges should align with your typical query patterns.Ensure that each partition contains a reasonable amount of data, neither too small nor too large.
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION YourPartitionFunction (DATETIME) AS RANGE LEFT FOR VALUES ('2022-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2024-01-01'); - Use Aligned Indexes:
- Ensure that indexes are aligned with the partitioning scheme to maximize performance.
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX YourClusteredIndex ON YourTable(YourPartitionColumn) ON YourPartitionScheme(YourPartitionColumn); - Consider Partition Elimination:
- Partition elimination can significantly improve query performance by skipping irrelevant partitions when executing queries.
SELECT * FROM YourTable WHERE YourPartitionColumn >= '2023-01-01' AND YourPartitionColumn < '2024-01-01'; - Regularly Maintain Partitions:
- Implement a maintenance plan to manage partitioning, including rebuilding indexes and updating statistics.
ALTER INDEX YourClusteredIndex ON YourTable REBUILD PARTITION = ALL; - Monitor Partition Usage:
- Regularly monitor the usage of partitions to identify potential performance bottlenecks or the need for adjustments.
SELECT partition_number, rows FROM sys.partitions WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID('YourTable'); - Use Partition Switching for Efficient Data Loading:
- If you frequently load and unload large amounts of data, consider using partition switching for efficient data movement.
ALTER TABLE StagingTable SWITCH TO YourTable PARTITION YourPartition; - Test and Optimize:
- Before implementing partitioning in a production environment, thoroughly test its impact on various types of queries and workloads to ensure performance gains.
Keeping Partitions Balanced
Balancing partitions helps distribute data evenly across the table, preventing hotspots and ensuring uniform performance.
Regular Maintenance Routines
Perform routine maintenance tasks, such as updating statistics and rebuilding indexes, to keep the partitioned table in optimal condition.
Backing Up and Restoring Partitioned Tables
Include partitioned tables in your backup and restore strategies. This is essential for data recovery and maintaining business continuity in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Real-world Use Cases of Partition Tables in SQL Server
Partition tables in SQL server find applications across various industries. Consider the following real-world scenarios where partitioning has proven to be invaluable:
- Financial Services: Managing vast transaction histories efficiently.
- E-commerce: Handling extensive product and sales data with ease.
- Healthcare: Storing and retrieving patient records seamlessly.
- Logistics: Tracking and analyzing shipment data effortlessly.