Contents
JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers PDF
JavaScript has become an integral part of web development, and mastering it is crucial for anyone aspiring to be a proficient web developer. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey, understanding the common interview questions and their answers can give you a significant edge. In this article, we will delve into Best JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers PDF provide comprehensive answers to help you prepare for your next JavaScript-focused interview. also you can download E-Book

- Q: What is JavaScript, and why is it essential in web development?
- A: JavaScript is a scripting language that enables interactive web pages. It’s essential as it allows for client-side interactions, enhancing user experiences.
- Q: Differentiate between
undefinedandnullin JavaScript.- A:
undefinedrepresents the absence of a value, often a variable that hasn’t been assigned.nullis an intentional absence of any object value.
- A:
- Q: Explain the concept of closure in JavaScript.
- A: Closures occur when a function retains access to variables from its outer scope, even after the outer function has finished execution.
- Q: How does prototypal inheritance work in JavaScript?
- A: JavaScript uses prototype chains for inheritance, where objects can inherit properties and methods from other objects through their prototype.
- Q: What is the significance of the keyword
thisin JavaScript?- A:
thisrefers to the current execution context. Its value depends on how a function is invoked, providing a way to access object properties or methods.
- A:
- Q: Explain the event bubbling and capturing phases in the DOM.
- A: Event bubbling is the default behavior where the innermost element’s event is handled first, then bubbles up. Capturing is the reverse, starting from the outermost element.
- Q: How does JavaScript handle asynchronous operations?
- A: JavaScript uses callbacks, promises, and async/await to handle asynchronous tasks, ensuring non-blocking execution and better code readability.
- Q: Differentiate between
let,const, andvarin variable declaration.- A:
letandconstare block-scoped, whilevaris function-scoped. Additionally,constcannot be reassigned, butletandvarcan.
- A:
- Q: What are arrow functions, and how do they differ from regular functions?
- A: Arrow functions are a concise syntax for writing functions in JavaScript. They don’t have their own
thisandargumentsbindings, making them suitable for certain use cases.
- A: Arrow functions are a concise syntax for writing functions in JavaScript. They don’t have their own
- Q: Explain the purpose of the
asyncandawaitkeywords in JavaScript.- A:
asyncis used to define asynchronous functions, andawaitis used to pause execution until a promise is settled, simplifying asynchronous code.
- A:
- Q: What is the role of the
localStorageandsessionStorageobjects in web development?- A: Both objects provide a way to store key-value pairs on the client-side.
localStoragepersists even after the browser is closed, whilesessionStorageis limited to the session.
- A: Both objects provide a way to store key-value pairs on the client-side.
- Q: How does event delegation work in JavaScript, and why is it useful?
- A: Event delegation involves assigning a single event listener to a common ancestor rather than individual elements. It’s useful for handling events on dynamic content efficiently.
- Q: What is the purpose of the JavaScript
mapfunction?- A: The
mapfunction is used to create a new array by applying a provided function to each element of an existing array, preserving the original array.
- A: The
- Q: Explain the same-origin policy and how it impacts JavaScript in web development.
- A: The same-origin policy restricts web pages from making requests to a different domain than the one that served the web page, preventing potential security vulnerabilities.
- Q: Describe the difference between
==and===in JavaScript.- A:
==performs type coercion, allowing different types to be compared after conversion.===strictly compares values without type conversion, ensuring both value and type equality.
- A:
- Q: What is the purpose of the JavaScript
setTimeoutfunction?- A:
setTimeoutis used to delay the execution of a function by a specified amount of time, allowing for asynchronous behavior and better control over timing.
- A:
- Q: How can you handle exceptions in JavaScript?
- A: Exceptions can be handled using try-catch blocks. Code within the try block is executed, and if an exception occurs, it’s caught and handled in the catch block.
- Q: What is the role of the JavaScript
fetchAPI?- A: The
fetchAPI is used to make network requests and handle responses. It provides a modern alternative to XMLHttpRequest, supporting promises and a simpler syntax.
- A: The
- Q: Explain the concept of hoisting in JavaScript.
- A: Hoisting involves the automatic movement of variable and function declarations to the top of their containing scope during the compilation phase.

- Q: What is the purpose of the JavaScript
reducefunction?- A: The
reducefunction is used to reduce an array to a single value by applying a specified function to each element and accumulating the result.
- A: The
- Q: How does the
localStoragediffer fromcookiesin web development?- A:
localStorageis a client-side storage solution for larger amounts of data, whilecookiesare primarily used for storing small pieces of data and have a smaller capacity.
- A:
- Q: Explain the concept of the event loop in JavaScript.
- A: The event loop is a mechanism that allows JavaScript to perform non-blocking operations by managing the execution of tasks in a single-threaded environment.
- Q: What is the purpose of the JavaScript
Promiseobject?- A:
Promiseis an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. It simplifies working with asynchronous code, making it more readable and maintainable.
- A:
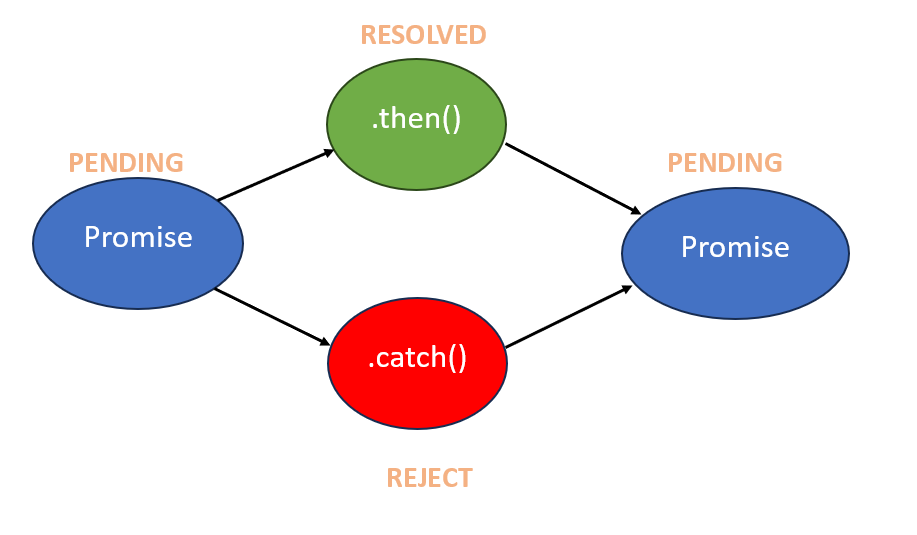
Promise object- Q: Differentiate between the
spliceandslicemethods in JavaScript.- A:
spliceis used to change the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing elements.slicecreates a shallow copy of a portion of an array without modifying the original array.
- A:
- Q: How does the JavaScript
addEventListenermethod work?- A:
addEventListeneris used to attach an event handler function to an HTML element. It enables the execution of specified code when a particular event occurs on the element.
- A:
- Q: Explain the difference between
let,var, andconstin variable declaration with example.- A :
letallows variable reassignment within the same scope.varis function-scoped and can be reassigned globally.constis block-scoped and cannot be reassigned.
- A :
var (variable):
Variables declared with var are function-scoped or globally-scoped.
They are hoisted to the top of their scope during the compilation phase.
var variables can be re-declared and updated.
function exampleVar() {
if (true) {
var x = 10;
console.log(x); // Outputs 10
}
console.log(x); // Outputs 10
}
let:
Variables declared with let are block-scoped, meaning they exist only within the block (enclosed by curly braces) where they are defined.
let variables are not hoisted to the top of their scope.
They can be reassigned, but not re-declared in the same scope.
function exampleLet() {
if (true) {
let y = 20;
console.log(y); // Outputs 20
}
// console.log(y); // ReferenceError: y is not defined (because y is not accessible here)
}
const (constant):
Variables declared with const are also block-scoped.
They must be initialized when declared and cannot be reassigned.
Like let, const variables are not hoisted.
function exampleConst() {
const z = 30;
// z = 40; // TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
console.log(z); // Outputs 30
}- 27. Q: What is the significance of closures in JavaScript?
- A: Closures allow functions to retain access to variables from their containing scope, even after the scope has finished execution.
function outer() {
let data = 'I am from outer function';
function inner() {
console.log(data);
}
return inner;
}
const closureExample = outer();
closureExample(); // Output: I am from outer function
- 28. Q: What is the purpose of the
thiskeyword in JavaScript?- A:
thisrefers to the object to which the current function or method belongs.
- A:
const person = {
name: 'John',
greet: function() {
console.log(`Hello, ${this.name}!`);
}
};
person.greet(); // Output: Hello, John!
- 29. Q: What is a promise in JavaScript? Provide an example.
- A: A promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation.
const fetchData = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Data fetched successfully');
}, 2000);
});
};
fetchData()
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
- 30. Q: Differentiate between
nullandundefinedin JavaScript.- A:
nullis an explicitly assigned empty value, whileundefinedsignifies a variable that has been declared but not assigned any value.
- A:
let x;
console.log(x); // Output: undefined
let y = null;
console.log(y); // Output: null
- 31. Q: How does prototypal inheritance work in JavaScript?
- A: Objects in JavaScript can inherit properties and methods from other objects through a prototype chain.
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Animal.prototype.makeSound = function() {
console.log(‘Some generic sound’);
};
function Dog(name, breed) {
Animal.call(this, name);
this.breed = breed;
}
Conclusion
Embarking on a journey to master JavaScript is both challenging and rewarding. Armed with the insights from these JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers PDF, you’re better equipped to showcase your expertise and navigate the challenges of a JavaScript-focused interview. Remember, continuous learning is key to staying at the forefront of web development. Download E-Book and if you have any question feel free to comments that
FAQs
- Q: How can I prepare for a JavaScript interview?
- A: Start by revisiting the foundational concepts, practice coding exercises, and familiarize yourself with common interview questions.
- Q: What is the significance of closures in JavaScript?
- A: Closures allow functions to retain access to variables from their containing scope, enhancing flexibility and privacy in code.
- Q: Which framework is better, React or Angular?
- A: The choice depends on the project requirements. React is more lightweight and flexible, while Angular offers a comprehensive framework with built-in features.
- Q: How does JavaScript handle asynchronous operations?
- A: JavaScript uses callbacks, promises, and async/await syntax to manage asynchronous code and ensure non-blocking execution.
- Q: Why is web security important in JavaScript development?
- A: Web security is crucial to protect user data and prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Feel free to use these JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers PDF e-book. Good luck!